how to convert aldehyde to alcohol Scheme 2. conversion of primary alcohol to aldehyde using tempo in a
In this post, we are going to explore the conversion of primary alcohol to aldehyde using TEMPO in a copper vial. This is an interesting chemical transformation that has various applications in organic chemistry.
Scheme 2: Conversion of Primary Alcohol to Aldehyde using TEMPO
The scheme shown below illustrates the conversion process:
 To perform this reaction, a primary alcohol is first oxidized to an aldehyde using a catalyst called TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-oxyl). TEMPO is a stable radical that acts as a catalyst in the oxidation process.
To perform this reaction, a primary alcohol is first oxidized to an aldehyde using a catalyst called TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-oxyl). TEMPO is a stable radical that acts as a catalyst in the oxidation process.
The reaction is typically carried out in the presence of a copper catalyst and an appropriate oxidizing agent. The copper catalyst helps in the regeneration of the TEMPO catalyst, allowing it to participate in subsequent oxidation reactions.
There are several oxidizing agents that can be used in this process. Some commonly used examples include hypochlorite (NaClO) and hypobromite (NaBrO). These oxidants help in the conversion of the alcohol to an aldehyde by removing a hydrogen atom from the alcohol molecule.
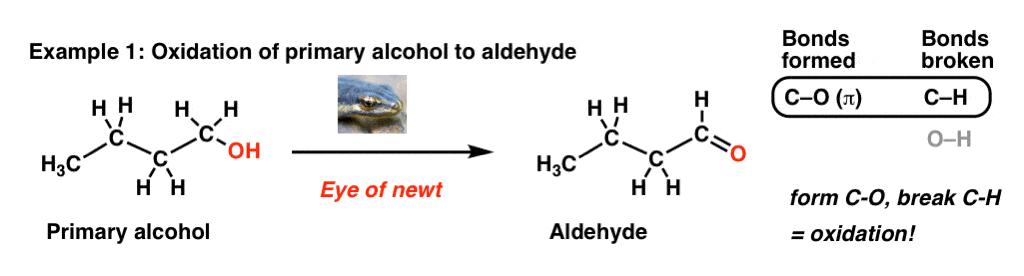
Alcohol Oxidation: “Strong” and “Weak” Oxidants
The oxidation of alcohols can be achieved using both “strong” and “weak” oxidants. The choice of oxidant depends on the desired selectivity and reaction conditions.
“Strong” oxidants, such as chromic acid (H2CrO4) or potassium permanganate (KMnO4), can completely oxidize a primary alcohol to its corresponding carboxylic acid. These oxidants are often used when a carboxylic acid is the desired product.
On the other hand, “weak” oxidants like TEMPO are more selective and can stop the oxidation reaction at the aldehyde stage. This selective oxidation is particularly useful when the aldehyde is the desired product. The use of TEMPO in combination with a copper catalyst allows for efficient and selective oxidation of primary alcohols to aldehydes.
Applications
The conversion of primary alcohols to aldehydes using TEMPO finds various applications in organic chemistry. One important application is in the synthesis of aldehydes for the production of pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals.
Aldehydes are versatile intermediates in organic synthesis and serve as precursors for a wide range of valuable compounds. By using TEMPO-based oxidation processes, chemists can efficiently convert primary alcohols to aldehydes, which can then be further elaborated into various targeted molecules.
Additionally, the selectivity of TEMPO-based oxidation reactions allows for the conversion of complex alcohol mixtures into specific aldehydes. This is particularly useful in the synthesis of natural products or in the modification of complex biomolecules.
In conclusion, the conversion of primary alcohol to aldehyde using TEMPO in a copper vial is an important process in organic chemistry. It offers a selective and efficient way to obtain aldehydes from primary alcohols, with various applications in pharmaceutical and fine chemical synthesis. The use of TEMPO as a catalyst, in combination with a copper catalyst and an appropriate oxidizing agent, allows for the controlled oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes. This process plays a significant role in the development of new drugs and the production of valuable chemical compounds.
If you are searching about Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Esters | General Chemistry you’ve visit to the right place. We have 5 Pics about Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Esters | General Chemistry like Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Esters | General Chemistry, Scheme 2. Conversion of primary alcohol to aldehyde using TEMPO in a and also Flow chart of oxidation process of alcohol ,aldehyde and carboxylic. Read more:
Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, And Esters | General Chemistry
 courses.lumenlearning.comcarboxylic acids esters aldehydes reaction alcohols atoms atom aldehyde ester ketones chem oxidation mugeek vidalondon bonded acetic ethanol acetate reacts
courses.lumenlearning.comcarboxylic acids esters aldehydes reaction alcohols atoms atom aldehyde ester ketones chem oxidation mugeek vidalondon bonded acetic ethanol acetate reacts
Alcohol Oxidation: “Strong” And “Weak” Oxidants — Master Organic Chemistry
 www.masterorganicchemistry.comoxidation aldehyde oxidants organik
www.masterorganicchemistry.comoxidation aldehyde oxidants organik
Flow Chart Of Oxidation Process Of Alcohol ,aldehyde And Carboxylic
 www.meritnation.comoxidation aldehyde carboxylic plzzzz
www.meritnation.comoxidation aldehyde carboxylic plzzzz
Solved: My Ketone Or Aldehyde Is: Camphor Alcohol That It | Chegg.com
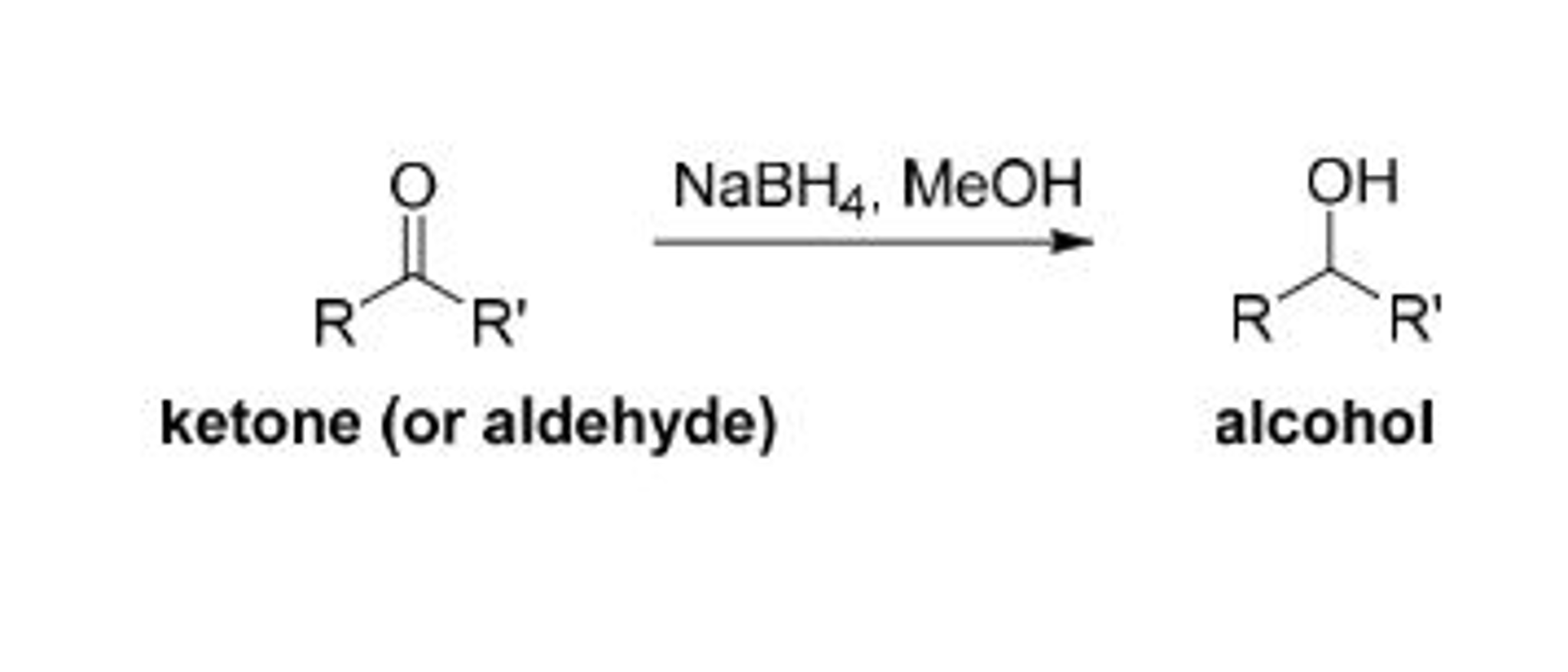 www.chegg.comaldehyde ketone camphor meoh nabh4 borneol
www.chegg.comaldehyde ketone camphor meoh nabh4 borneol
Scheme 2. Conversion Of Primary Alcohol To Aldehyde Using TEMPO In A
 www.researchgate.netaldehyde tempo scheme vial
www.researchgate.netaldehyde tempo scheme vial
Alcohol oxidation: “strong” and “weak” oxidants — master organic chemistry. Scheme 2. conversion of primary alcohol to aldehyde using tempo in a. Solved: my ketone or aldehyde is: camphor alcohol that it