what are the 4 types of polysaccharides Polysaccharides polysaccharide cellulose starch glycogen between difference examples glucose structure function food carbohydrates polymers sugar bioninja analysis functions lipids monosaccharides
Polysaccharides play a vital role in the world of chemistry and biology, serving as essential compounds in various organisms. These complex carbohydrates consist of long chains of monosaccharide units bonded together. They are abundant in nature and serve as a valuable energy source for living beings. In this post, we will explore the fascinating world of polysaccharides and their classification.
Understanding Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides are macromolecules made up of repeating units of monosaccharides. These long chains can contain hundreds or even thousands of sugar molecules joined by glycosidic bonds. The most common monosaccharides found in polysaccharides are glucose, fructose, and galactose.
 Polysaccharides exhibit a wide range of properties and functions in biological systems. These diverse roles include energy storage, structural support, cell recognition, and cell adhesion. The specific function of a polysaccharide depends on its structure and arrangement of monosaccharide units.
Polysaccharides exhibit a wide range of properties and functions in biological systems. These diverse roles include energy storage, structural support, cell recognition, and cell adhesion. The specific function of a polysaccharide depends on its structure and arrangement of monosaccharide units.
Classification of Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides can be classified into different categories based on their chemical structure and biological function. Let’s explore some of the major types:
Starch
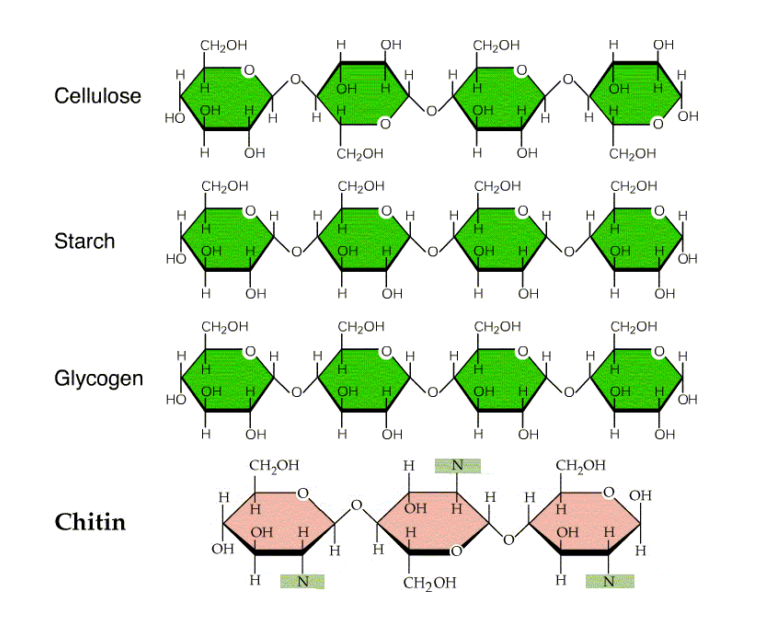
 Starch is a polysaccharide commonly found in plants. It serves as the primary energy storage molecule in plants, providing a readily available source of glucose. Starch is composed of two types of glucose polymers: amylose, which forms a linear structure, and amylopectin, which has a branched structure. Humans and animals can also digest starch to extract glucose for energy.
Starch is a polysaccharide commonly found in plants. It serves as the primary energy storage molecule in plants, providing a readily available source of glucose. Starch is composed of two types of glucose polymers: amylose, which forms a linear structure, and amylopectin, which has a branched structure. Humans and animals can also digest starch to extract glucose for energy.
Cellulose
 Cellulose is another vital polysaccharide found in the cell walls of plants. Unlike starch, cellulose cannot be digested by humans and most animals due to the lack of specific enzymes. However, it plays a crucial role in providing structural support and rigidity to plant cells. Cellulose fibers are widely used in the production of paper, textiles, and various other products.
Cellulose is another vital polysaccharide found in the cell walls of plants. Unlike starch, cellulose cannot be digested by humans and most animals due to the lack of specific enzymes. However, it plays a crucial role in providing structural support and rigidity to plant cells. Cellulose fibers are widely used in the production of paper, textiles, and various other products.
Glycogen
Glycogen is the main storage form of glucose in animals and humans. It is primarily stored in the liver and skeletal muscles and serves as an energy reserve for the body. Glycogen is a highly branched polysaccharide, allowing for rapid glucose release when energy demands increase.
The Significance of Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides are of immense importance in various fields. In the food industry, they serve as thickeners, stabilizers, and emulsifiers. Polysaccharides like chitosan and alginate have applications in drug delivery systems and wound healing due to their biocompatible and biodegradable nature. Moreover, polysaccharides play a vital role in shaping the physical properties of many substances, including gels, creams, and foams.
In conclusion, polysaccharides are remarkable compounds that contribute to the structure, function, and energy storage in living organisms. Their diverse range of properties and classifications make them an intriguing subject of study. Understanding polysaccharides not only enhances our knowledge of fundamental biology but also opens avenues for their application in various industries.
If you are searching about Polysaccharides | Types, Definition, Structure, Foods you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pics about Polysaccharides | Types, Definition, Structure, Foods like Polysaccharides: Definition, Types, Features, Significance - Embibe, Polysaccharides: What are Polysaccharides and its Classify? and also The 3 Polysaccharides Defined: Function, Benefits, and Food Examples. Here you go:
Polysaccharides | Types, Definition, Structure, Foods
 alevelbiology.co.ukpolysaccharides glycogen starch cellulose carbohydrates structure chain fiber types look biology bio hexagons amylose cell three introduction notes many libretexts
alevelbiology.co.ukpolysaccharides glycogen starch cellulose carbohydrates structure chain fiber types look biology bio hexagons amylose cell three introduction notes many libretexts
Polysaccharides: What Are Polysaccharides And Its Classify?
 biochemden.compolysaccharides cellulose classified classification
biochemden.compolysaccharides cellulose classified classification
Polysaccharides: Definition, Types, Features, Significance - Embibe
 www.embibe.compolysaccharides
www.embibe.compolysaccharides
The 3 Polysaccharides Defined: Function, Benefits, And Food Examples
 medicinalherbals.netpolysaccharides polysaccharide cellulose starch glycogen between difference examples glucose structure function food carbohydrates polymers sugar bioninja analysis functions lipids monosaccharides
medicinalherbals.netpolysaccharides polysaccharide cellulose starch glycogen between difference examples glucose structure function food carbohydrates polymers sugar bioninja analysis functions lipids monosaccharides
Polysaccharides: What Are Polysaccharides And Its Classify?
 biochemden.compolysaccharides linkages sugars glycosidic monosaccharides uronic acids classification
biochemden.compolysaccharides linkages sugars glycosidic monosaccharides uronic acids classification
Polysaccharides cellulose classified classification. Polysaccharides glycogen starch cellulose carbohydrates structure chain fiber types look biology bio hexagons amylose cell three introduction notes many libretexts. Polysaccharides polysaccharide cellulose starch glycogen between difference examples glucose structure function food carbohydrates polymers sugar bioninja analysis functions lipids monosaccharides