why no ketoacidosis in type 2 diabetes Diabetic exchange: diabetic ketoacidosis treatments
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious condition that can affect individuals who have diabetes. It occurs when there is a shortage of insulin in the body, causing high blood sugar levels, along with the presence of ketones. Ketones are produced as a result of the body breaking down fat for energy instead of glucose. DKA can be life-threatening if not treated promptly, so it is essential for individuals with diabetes to be aware of the symptoms and seek medical help as soon as possible.
What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis is a complication that primarily affects individuals with type 1 diabetes, although it can also occur in individuals with type 2 diabetes. It typically occurs when the body does not have enough insulin to convert glucose into energy. Without insulin, the body starts breaking down fat for energy, which leads to the production of ketones.
 These ketones gradually build up in the blood, making it more acidic. As a result, the individual may start experiencing various symptoms such as frequent urination, extreme thirst, dry mouth, fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
These ketones gradually build up in the blood, making it more acidic. As a result, the individual may start experiencing various symptoms such as frequent urination, extreme thirst, dry mouth, fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Aldosterone in DKA
Aldosterone is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands that helps regulate the body’s fluid and electrolyte balance. During DKA, aldosterone levels can be significantly affected. Studies have found that individuals with DKA often have lower levels of aldosterone, which can contribute to the imbalance of fluids and electrolytes in the body.
 This fluid and electrolyte imbalance can lead to symptoms such as increased thirst, dehydration, and electrolyte abnormalities. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor aldosterone levels in individuals with DKA to ensure proper management of the condition.
This fluid and electrolyte imbalance can lead to symptoms such as increased thirst, dehydration, and electrolyte abnormalities. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor aldosterone levels in individuals with DKA to ensure proper management of the condition.
Treatment and Prevention of DKA
If you suspect that you or someone you know is experiencing DKA, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Treatment typically involves hospitalization, where fluids and electrolytes are replenished intravenously to correct the imbalances caused by DKA. Insulin is also administered to regulate blood sugar levels and stop the production of ketones.
Prevention of DKA involves consistent management of diabetes and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. Taking insulin as prescribed, following a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and staying hydrated can help prevent DKA episodes.
Conclusion
Diabetic Ketoacidosis is a serious complication that can occur in individuals with diabetes. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention is of utmost importance. Remember to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly, take insulin as prescribed, and consult with your healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive management plan to prevent DKA and maintain optimal health.
If you are searching about Diabetic Ketoacidosis | EKF Diagnostics - Stanbio you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Pictures about Diabetic Ketoacidosis | EKF Diagnostics - Stanbio like SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow, Diabetic Ketoacidosis | EKF Diagnostics - Stanbio and also Absorb Medicine: Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA). Here it is:
Diabetic Ketoacidosis | EKF Diagnostics - Stanbio
 www.ekfusa.comketoacidosis hydroxybutyrate diabetic beta dka bhb test glucose blood insulin levels why liver illustration cells than
www.ekfusa.comketoacidosis hydroxybutyrate diabetic beta dka bhb test glucose blood insulin levels why liver illustration cells than
SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow
www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic diabetic inhibitor induced pathophysiology dka urine renalfellow renal sediment mitochondria acidosis immunologic transplantation principles bacterial variant
Aldosterone In Dka | DiabetesTalk.Net
 diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic diabetes type ketosis pediatric dka starvation population insulin figure symptoms signs aldosterone diabetestalk quizlet sign
diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic diabetes type ketosis pediatric dka starvation population insulin figure symptoms signs aldosterone diabetestalk quizlet sign
Absorb Medicine: Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
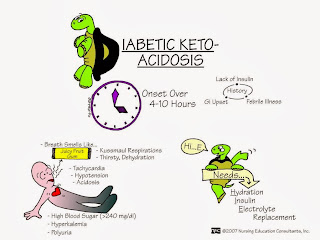 absorbmedicine.blogspot.comketoacidosis diabetic dka insulin diabetes
absorbmedicine.blogspot.comketoacidosis diabetic dka insulin diabetes
Diabetic Exchange: Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatments
 diabeticexchange.blogspot.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes nursing type treatment mechanism ketosis vs symptoms nurse ketogenic sepsis notes signs sugar cancer body memory
diabeticexchange.blogspot.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes nursing type treatment mechanism ketosis vs symptoms nurse ketogenic sepsis notes signs sugar cancer body memory
Diabetic ketoacidosis. Ketoacidosis diabetic dka insulin diabetes. Ketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes nursing type treatment mechanism ketosis vs symptoms nurse ketogenic sepsis notes signs sugar cancer body memory